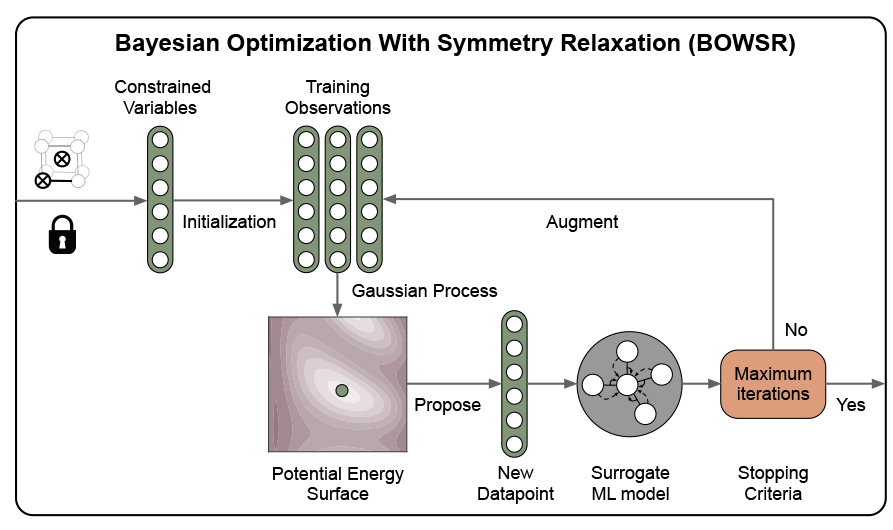
Efficient near-infrared phosphors
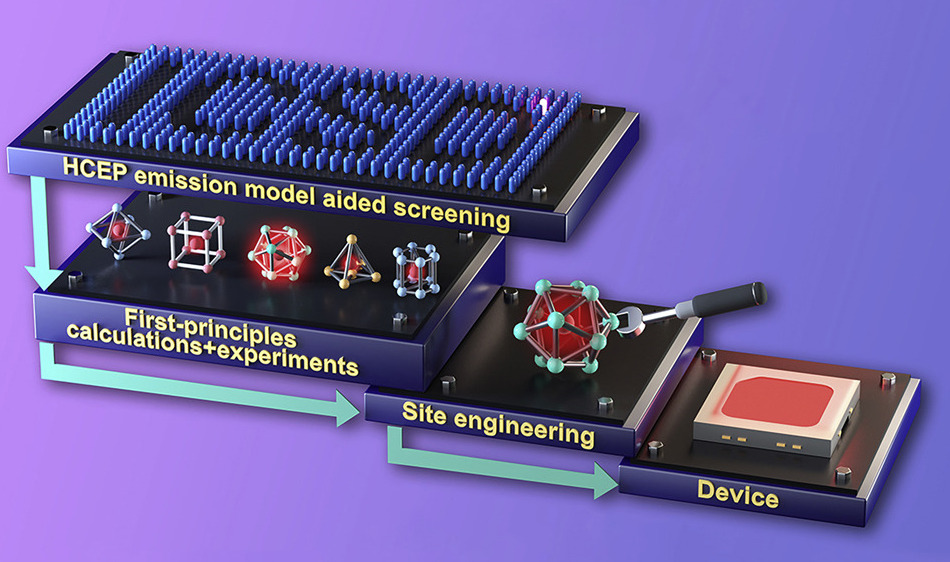
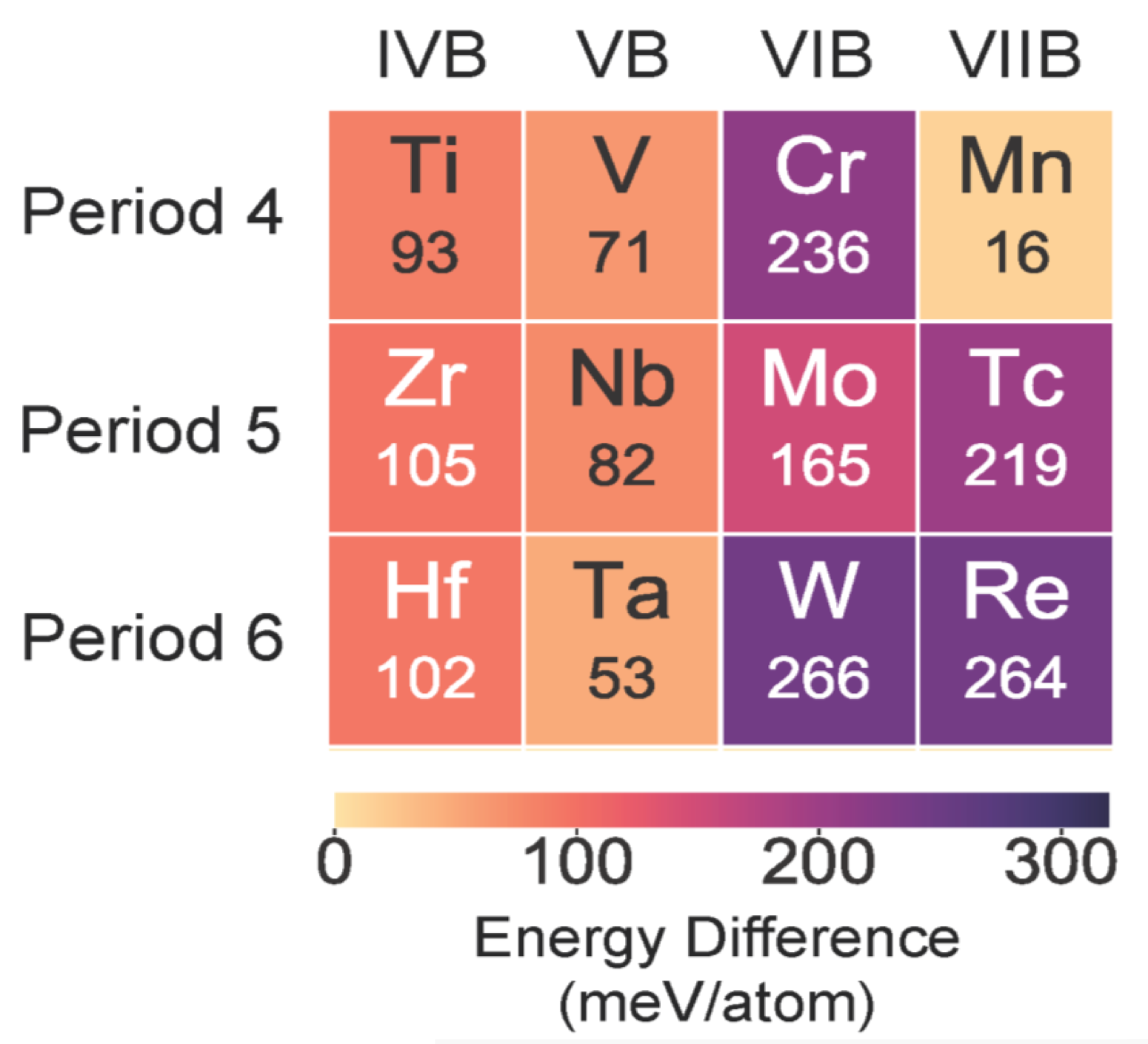
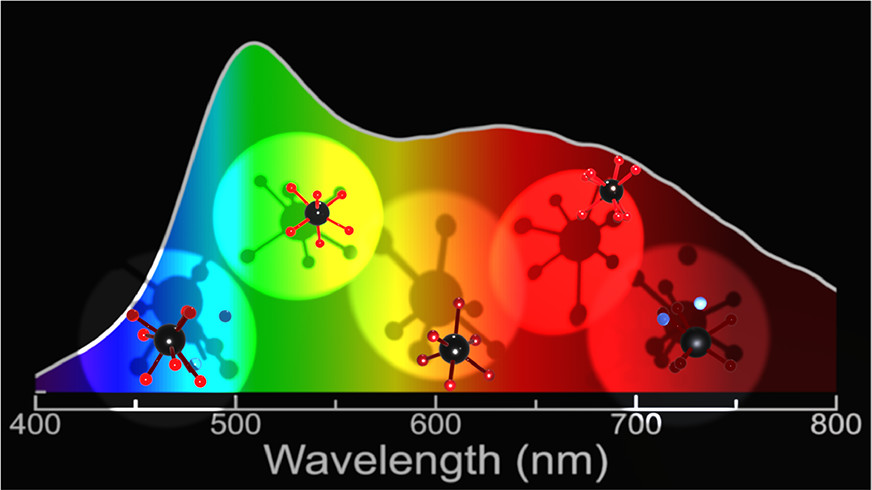
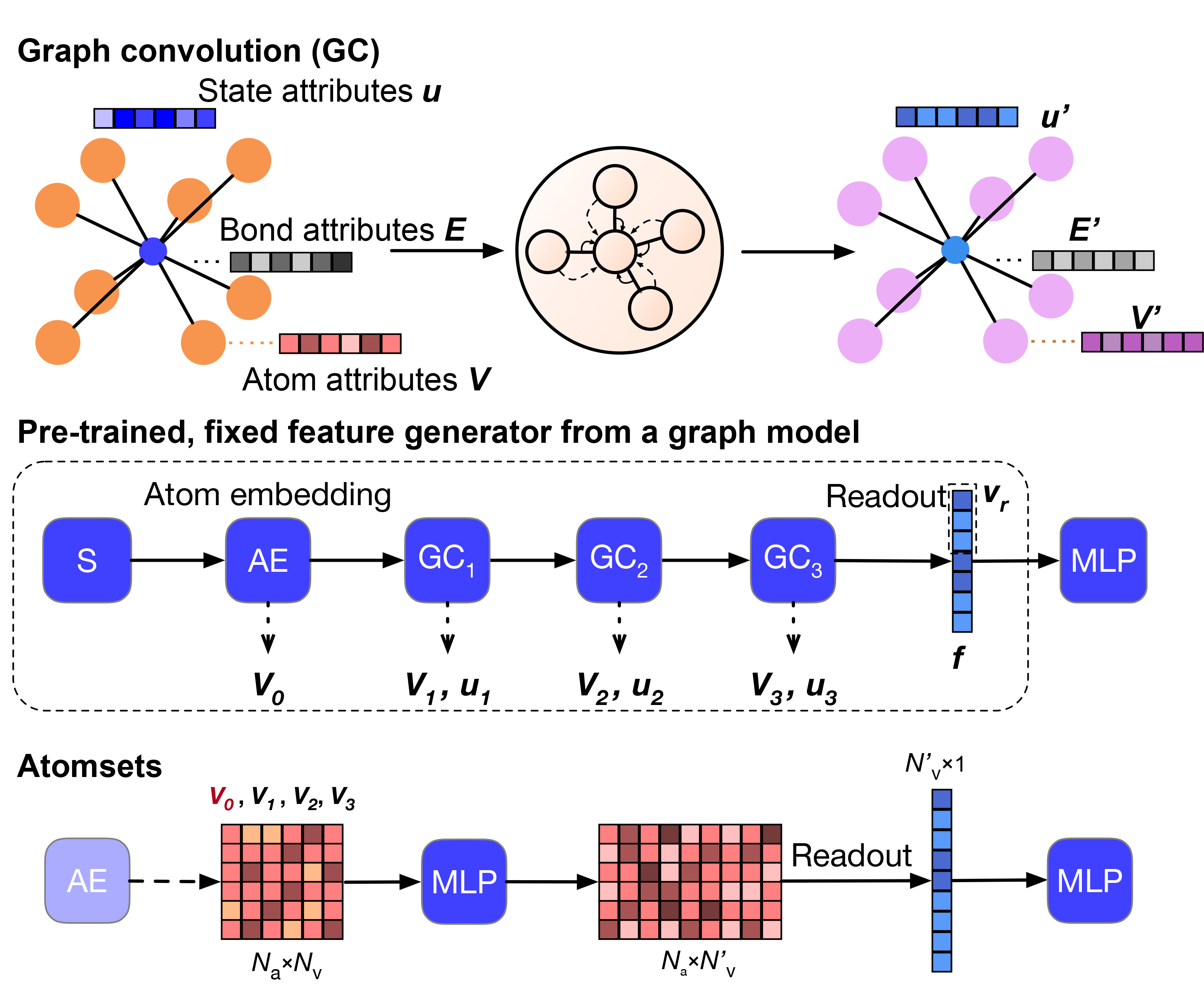
Efficient near-infrared (NIR) LEDs are used in many applications, including medical diagnostics, food detection, security monitoring, and machine vision. In this collaborative work with the group of Prof Rong-jun Xie at Xiamen University published in Matter, Mahdi Amachraa developed descriptors of the Eu(II)-host interactions to predict the 5d-to-4f energy gap with a RMSE of 7.0 nm. By incorporating this predictor into a high-throughput screening of 223 nitride materials in the Inorganic Crystal Structure Database, we identified and experimentally validated (Sr,Ba)3Li4Si2N6:Eu(II) with NIR emissions of 800- 830 nm and high quantum efficiencies (QEs) of 30%-40%. This NIR emitter has 3x more power than prevailing NIR emitters. We demonstrate that the ultralong emission wavelength and high QE stem from a coordinated energy transfer and an optimized electronic delocalization around Eu(II). Check out this work here.